A class of proteins known as TMEM16 scramblases permit rearrangement of lipids in the cell membrane chiefly by thinning the membrane, according to a new model by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The model, based on the highest-resolution images to date of a TMEM16 scramblase, challenges the prevailing theory of how these proteins play their fundamental role in biology and could lead to the first scramblase-targeted pharmaceuticals.
Scramblase proteins reside in the outer membranes of virtually all eukaryotic cells and can disorganize—scramble—the normal arrangement of fat-related lipid molecules that constitute the membranes. This disruption of the normal membrane structure is a necessary part of many important biological events including blood coagulation, membrane repair and apoptosis, the programmed death of damaged cells. Dysfunctions of TMEM16 scramblases have been linked to blood and bone disorders, lower sperm motility, cancers and movement disorders, among other conditions.
The researchers, whose findings were reported May 11 in Nature Communications, used cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to image the structure of a TMEM16 scramblase at near-atomic-scale resolution in a membrane-like environment. The image data suggested strongly that what had been the consensus model of how these scramblases work needs to be revised.
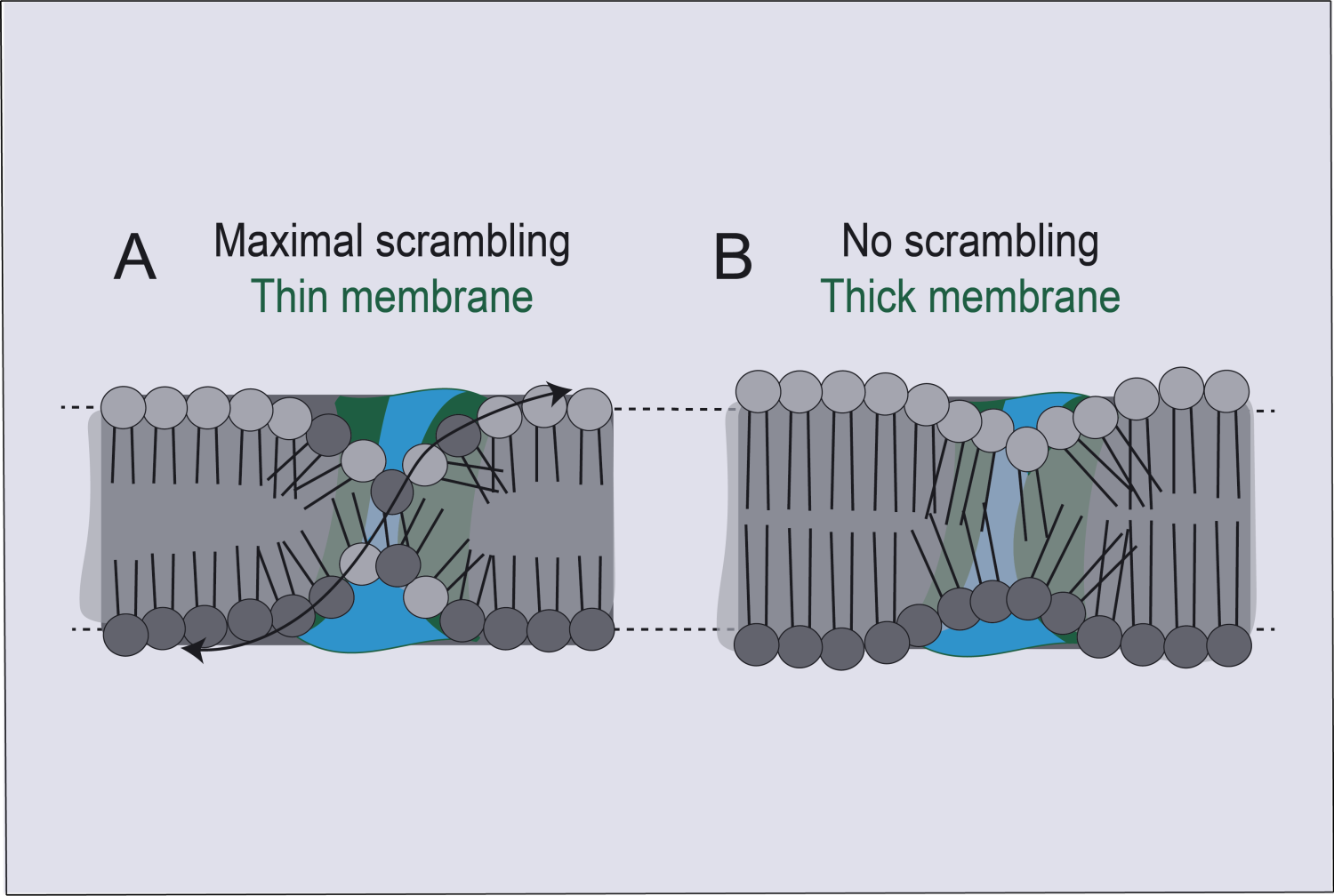
“We’re proposing that the TMEM16 scramblase protein works not by interacting directly with specific lipids, but instead by mechanically altering the structure of the membrane, making it generally very thin and disordered,” said Dr. Alessio Accardi, professor of physiology and biophysics in anesthesiology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The first authors of the study were Dr. Maria Falzone, a PhD candidate in the Accardi lab during the study, and Dr. Zhang Feng, a postdoctoral associate in the Accardi lab.
The outer membrane of a cell is composed of two tightly ordered layers of lipid molecules, where the outer and inner layers are composed of distinct sets of lipid molecule types. A TMEM16 scramblase spans these layers and has a tube or “chute” structure, which opens when activated by binding of calcium ions.
Activation of this protein causes lipids in the cell membrane to lose their normal arrangement and to become randomly distributed between the two layers. The dominant hypothesis had been that the chute acts somewhat like the groove in a credit card-swipe reader with lipids freely moving between membrane layers by fitting into the groove head-first, thus causing the two membrane leaflets to lose their usual ordering. However, the difficulty of resolving TMEM16’s structure in complex with weakly associated lipid molecules in sufficient detail with imaging methods had left the precise mechanism of lipid scrambling unclear.
Dr. Accardi and his team used cryo-EM to build a 3D structural image of the TMEM16 scramblase found in a species of fungus, Aspergillus fumigatus. This version of the scramblase is very similar to the human proteins, though it is more stable for cryo-EM purposes. The resolution of the structural image was 2.4 Angstroms, or about a quarter of a billionth of a meter—the highest resolution to date for a TMEM16 scramblase structure.
The structural imaging data, combined with functional analyses of different mutants of the TMEM16 scramblase, implied that the card-swipe reader model is incorrect. Instead of having specific interactions with lipids, the scramblase chute locally deforms the membrane to make it significantly thinner, disorganizing lipids in the vicinity.
“We’re proposing that TMEM16 scramblase mechanically alters the structure of the membrane, making it very thin and disordered near the groove,” Dr. Accardi said. “This enables lipid movement without necessitating interactions with the inside of the groove, as in the credit card reader model.”
Opening of the chute, he noted, also brings in water molecules which facilitate the movement of the nearby lipid heads between the membrane layers.
Dr. Accardi and his team are now working to confirm their findings in mammalian versions of TMEM16 scramblases. They are also studying how these scramblases’ functions are regulated in cells, and are starting to think about how future small-molecule drugs could restore or otherwise alter scramblase function to treat diseases.
“We’re trying to understand the implications, for biology and medicine, of this new model suggested by our study,” Dr. Accardi said.

